MacOS Mojave 10.14.1
MicroPython 1.9.4.8
Goals:
- Use Python for Microcontrollers (MicroPython) on Wemos D1 mini (ESP8266) and ESP32.
Info:
- MicroPython is a condensed, optimized code of Python 3 that has been loaded in hardware. This means rather than having to have an interpreter run on an operating system to execute the Python code, the MicroPython chip can run the Python code directly on the hardware. No operating system is needed. In fact, MicroPython has basic file I/O built in.
- After a fresh install and boot the device configures itself as a WiFi access point (AP) that you can connect to. The ESSID is of the form MicroPython-xxxxxx where the x’s are replaced with part of the MAC address of your device (so will be the same every time, and most likely different for all ESP8266 chips). The password for the WiFi is micropythoN (case-sensitive). Its IP address will be 192.168.4.1 once you connect to its network.
Installing Micropython:
- Install the latest EspTool (2.5.0+):
- Windows: using Windows Terminal (cmd):
- For using ESP32 on WIndows we need to install USB Driver:
- Download the driver and follow the instructions here.
- pip install esptool --upgrade
- pip3 install adafruit-ampy --upgrade
- set AMPY_PORT=COM?
- Linux:
- sudo pip install esptool --upgrade
- pip3 install adafruit-ampy --upgrade
- export AMPY_PORT=/dev/ttyUSB0
- MacOS: using Terminal:
- pip3 install esptool --upgrade
- pip3 install adafruit-ampy --upgrade
- export AMPY_PORT=/dev/tty.usbserial-1420
- For using ESP32 on MacOS we need to install USB Driver:
- Download Legacy MacVCP USB to Serial driver
- Install SiLabsUSBDriverDisk.dmg
- Restart MacOS
- After restart, a new device will be detected (e.g: dev/tty.SLAB_USBtoUART)
- Erase the flash (ESP8266 and ESP32):
- Windows:
- locate the latest esptool.py installed:
- cd \
- dir /S esptool.py
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --port COM? erase_flash
- Linux:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash
- MacOS:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --port /dev/tty.usbserial-1420 erase_flash
- Deploy the new firmware on ESP8266:
- Download MicroPython image here:
- Windows:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --port COM? --baud 460800 write_flash --verify -fs=detect -fm dio 0 \users\Marcus\Downloads\esp8266-20180511-v1.9.4.bin
- Linux:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --baud 460800 write_flash --verify -fs=detect -fm dio 0 /home/marcus/esp8266-20180511-v1.9.4.bin
- MacOS:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --port /dev/tty.usbserial-1420 --baud 460800 write_flash --verify -fs=detect -fm dio 0 /Users/marcus/Downloads/esp8266-20180511-v1.9.4.bin
- Deploy the new firmware on ESP32:
- Download MicroPython image here:
- Windows:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --chip esp32 --port COM4 write_flash -z 0x1000 \users\Marcus\Downloads\esp32-20180730-v1.9.4-410-g11a38d5dc.bin
- Linux:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 write_flash -z 0x1000 /home/marcus/esp32-20180730-v1.9.4-410-g11a38d5dc.bin
- MacOS:
- python <esptool-path>/esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/tty.SLAB_USBtoUART write_flash -z 0x1000 /Users/marcus/Downloads/esp32-20180730-v1.9.4-410-g11a38d5dc.bin
- Installing Libraries not included in MicroPython using upip and REPL:
- Connecting to Internet:
- import network
- station = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
- station.active(True)
- station.connect('ssid', 'password')
- print('Connected: {}'.format(station.isconnected()))
- ipadd=station.ifconfig()
- print('IP: {}'.format(ipadd))
- import upip
- Use upip to install any library available on PyPI:
- upip.install('micropython-umqtt.robust')
- upip.install('micropython-umqtt.simple')
- List files on the board using Ampy, MFPShell or RShell:
- ampy ls (needs AMPY_PORT env var)
- mpfshell
- open tty.SLAB_USBtoUART
- ls
- rshell
- ls -l
- Connect and interact with a MicroPython board using a serial connection.
- Connect with the Device REPL using a terminal. The baudrate of the REPL is 115200 (Data: 8 bit; Parity: None; Stop bits: 1 bit; Flow Control: None):
- Windows:
- Use Putty or any other terminal software.
- Linux:
- ToDo
- MacOS:
- miniterm.py /dev/tty.usbserial-1420 115200
- Press Enter and the terminal should show Python prompt like >>>
- Try a Hello World:
- print("Hello World")
- import esp
- esp.flash_size()
- import uos
- uos.listdir()
- Blink Example:
- from machine import Pin
- import utime as time
- led_builtin = 2 # D4=gpio02
- led = Pin(led_builtin, Pin.OUT)
- while True:
- led.on()
- time.sleep(1)
- led.off()
- time.sleep(1)
- You can use the Arduino IDE to upload your C/C++ software to the ESP boards, even after the upload of the MicroPython firmware. You don't need to upload the original Expressif default firmware to use the Arduino IDE. However, if you really wants to upload the Expressif firmware, then these as the instructions for reverting board to the original Expressif default firmware to use with arduino C/C++ language:
- Download ESP Flash Tool
- ESP8266
- Download and extract the latest firmware (for ESP8266)
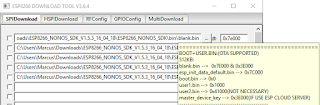
- Execute ESP Flash tool and select the right board: (e.g., <downloads>/flash_download_tool_v3.6.4/ESPFlashDownloadTool_v3.6.4.exe)
- ESP8266_NONOS_SDK-master/bin/blank.bin at 0x7E000 and 0x3E000
- ESP8266_NONOS_SDK-master/bin/esp_init_data_default_v08.bin at 0x7C000
- ESP8266_NONOS_SDK-master/bin/boot_v1.7.bin at 0x0
- ESP8266_NONOS_SDK-master/bin/at/1024+1024/user1.2048.new.5.bin at 0x1000
- ESP32:
- Choose the right COM port
- Choose Baud Rate 460800
- Click "Start" button.
- EsPy IDE - for Windows - Micropython IDE for ESP8266
- uPyLoader - for Windows - File transfer and communication tool for MicroPython boards
- Adafruit MicroPython Tool - for MacOS, Linux and Windows - Utility to interact with a MicroPython board over a serial connection.
- MPFShell - A simple shell based file explorer for ESP8266 and WiPy Micropython based devices - for MacOS and Linux
- RShell - Remote MicroPython shell - for MacOS and Linux
References:
- Getting started with MicroPython on the ESP8266
- Getting a MicroPython REPL prompt
- Announcing the MicroPython Plugin for PyCharm
- General information about the ESP8266 port